RAID 0 is a disk array that requires two disks of the same model and capacity to be used. By combining the two disks into one storage medium, read and write operations can be processed in parallel. This maximizes both capacity and read/write performance, with the speed potentially increasing by multiples. RAID 0 is the fastest disk array in terms of speed.
Introduction
On the user interface, the maximum size of a virtual disk that can be created is 16TB. When users need storage space larger than 16TB, it is not possible to directly create a single virtual disk. In certain use cases (e.g., video editing cache), where both large capacity and high-speed read/write performance are required, RAID 0 can be used to meet the need. This article will guide you on how to create RAID 0 to achieve these requirements.
Prerequisites
This experiment uses a Windows Server virtual compute instance and SSDs:
1. Windows Server 2019
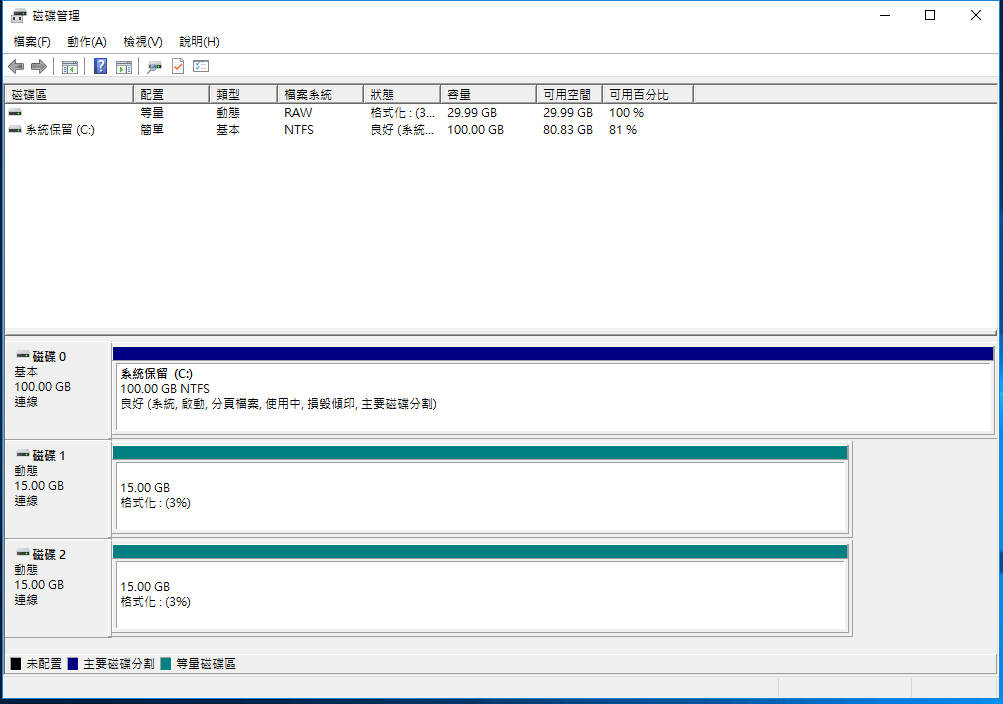
2. Virtual Disk Service (VDS) 18TB (9TB + 9TB)
Detailed Steps
STEP 1 Log in to Windows Server 2019
For login instructions, please refer toConnecting to a Windows Instance.
STEP 2 Open Disk Management
On the virtual compute instance, open Run and type Diskmgmt.msc
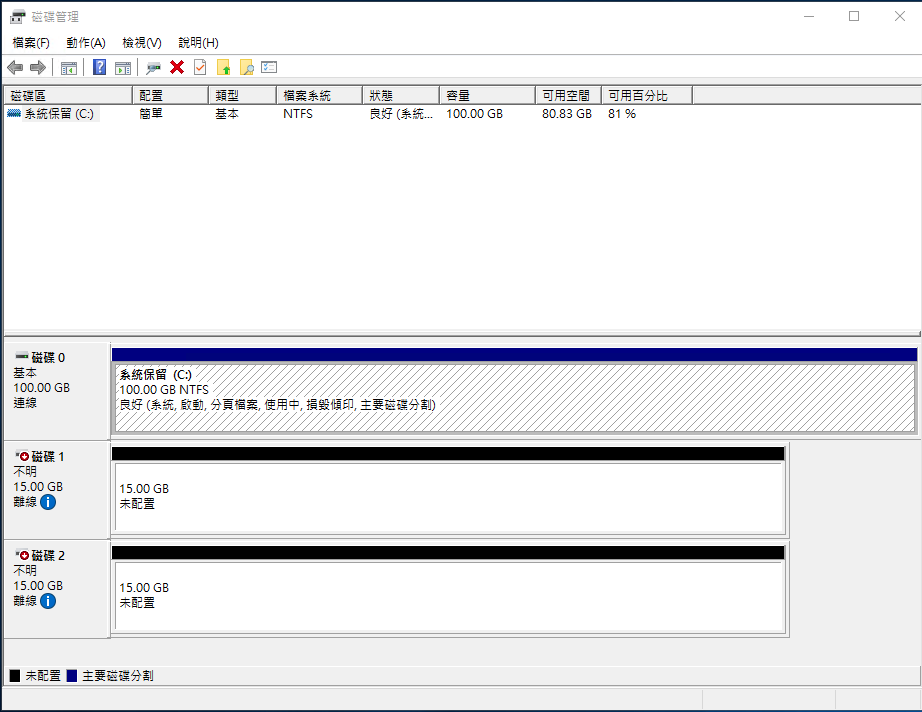
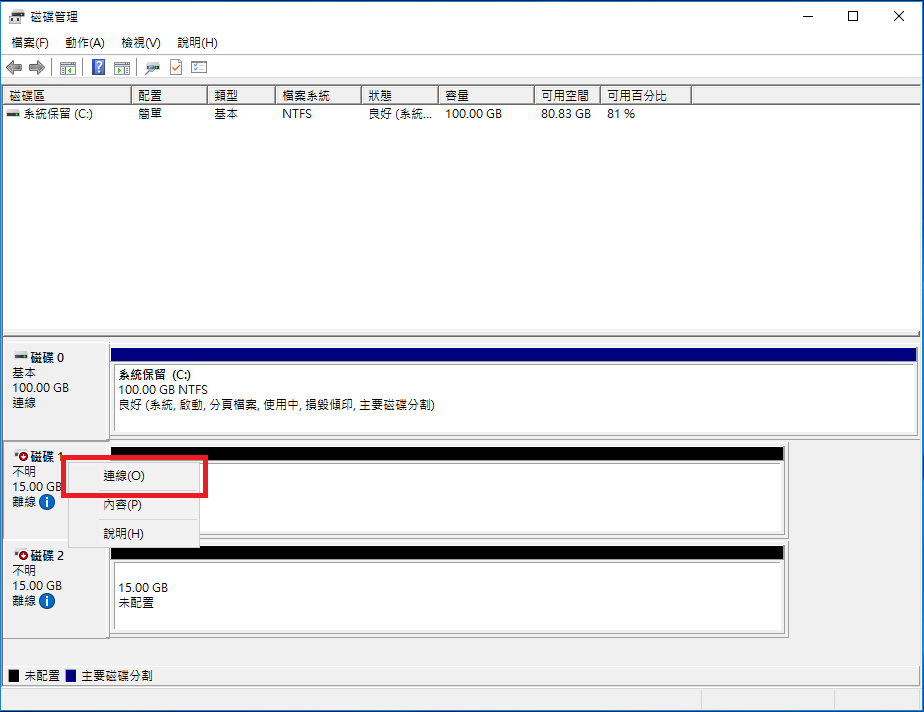
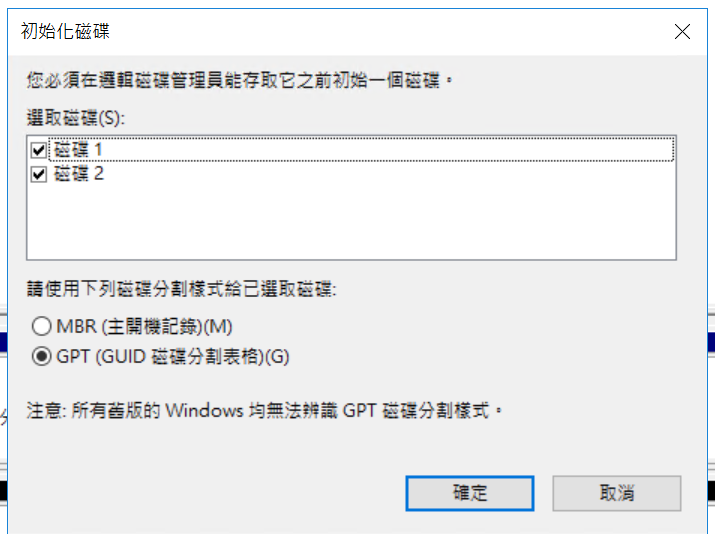
STEP 3 Initialize the Disks
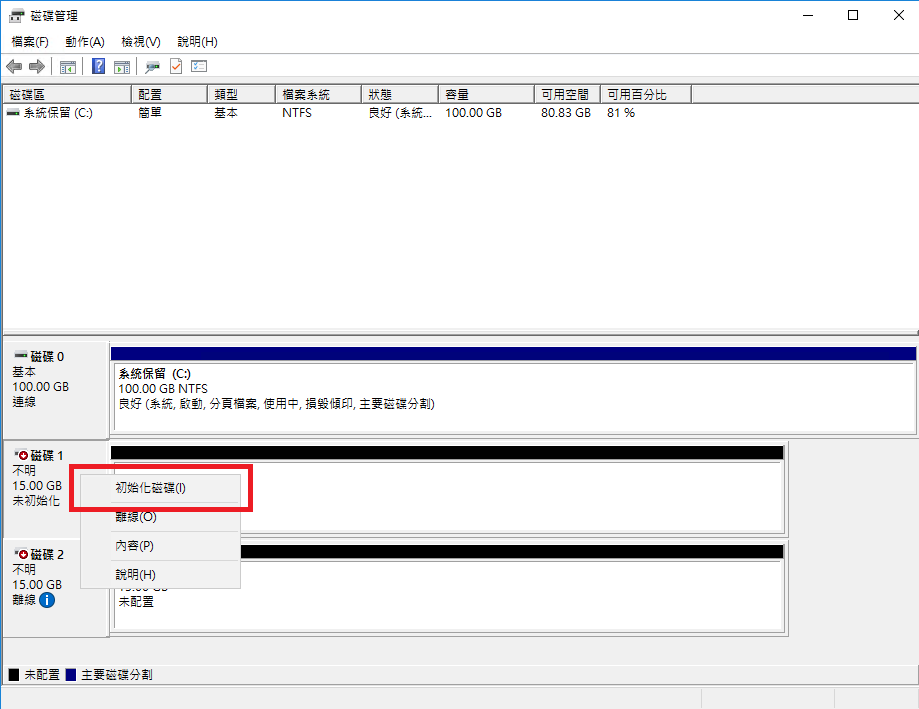
Right-click on the disk and select Initialize.
Initialize the disk:
Select GPT (GUID Partition Table):
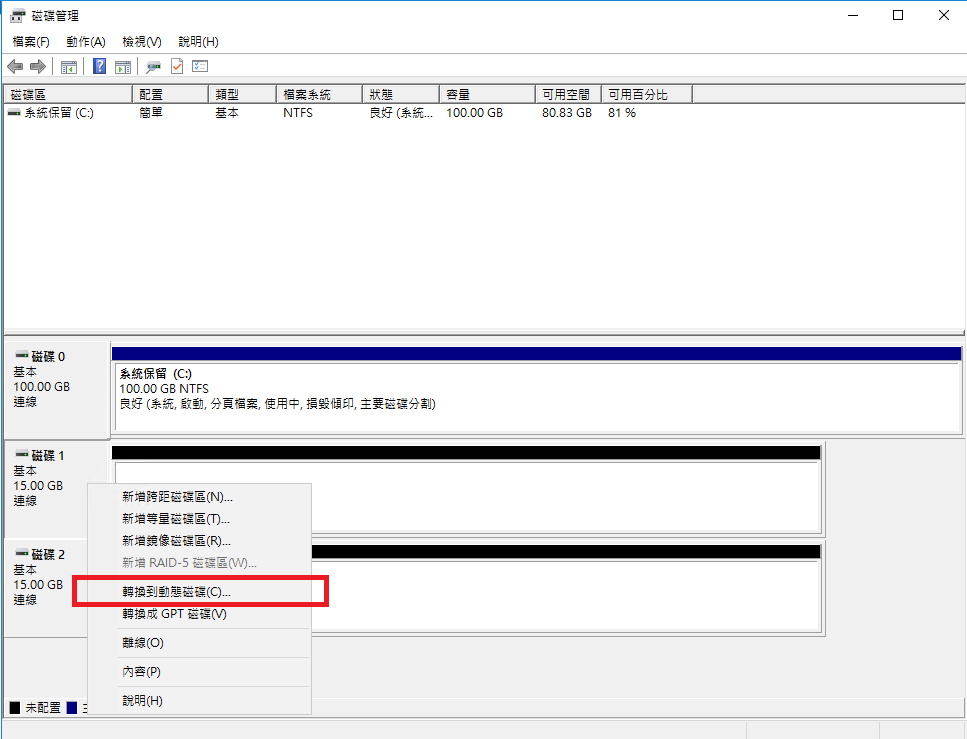
STEP 4 Convert to Dynamic Disk
Right-click and select Convert to Dynamic Disk.
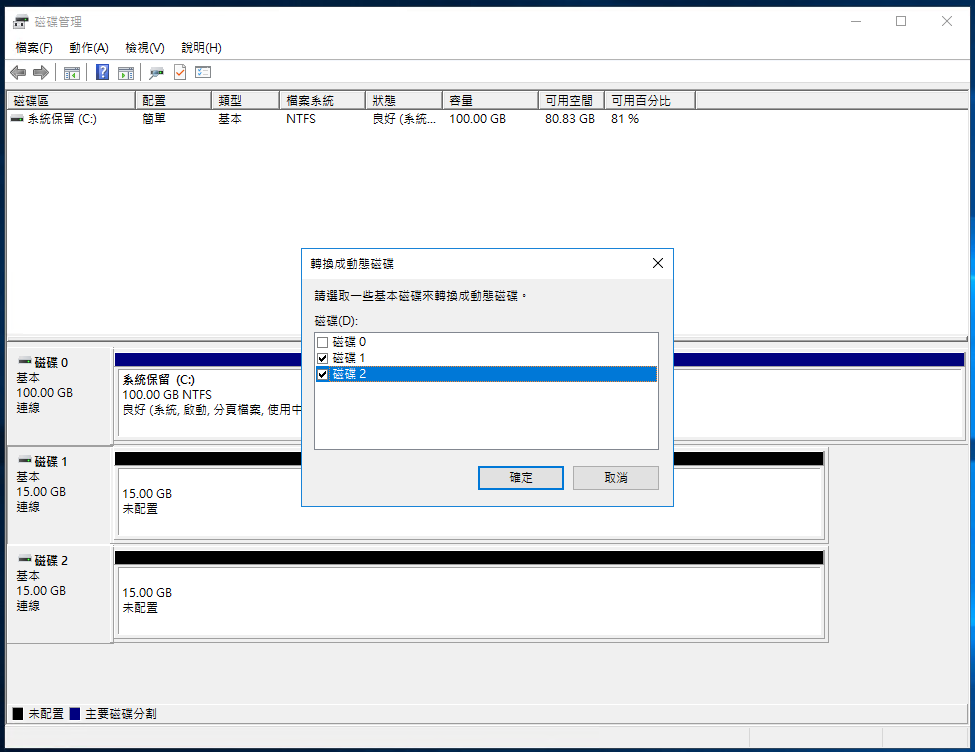
Select Disk 1 and Disk 2, then click OK.
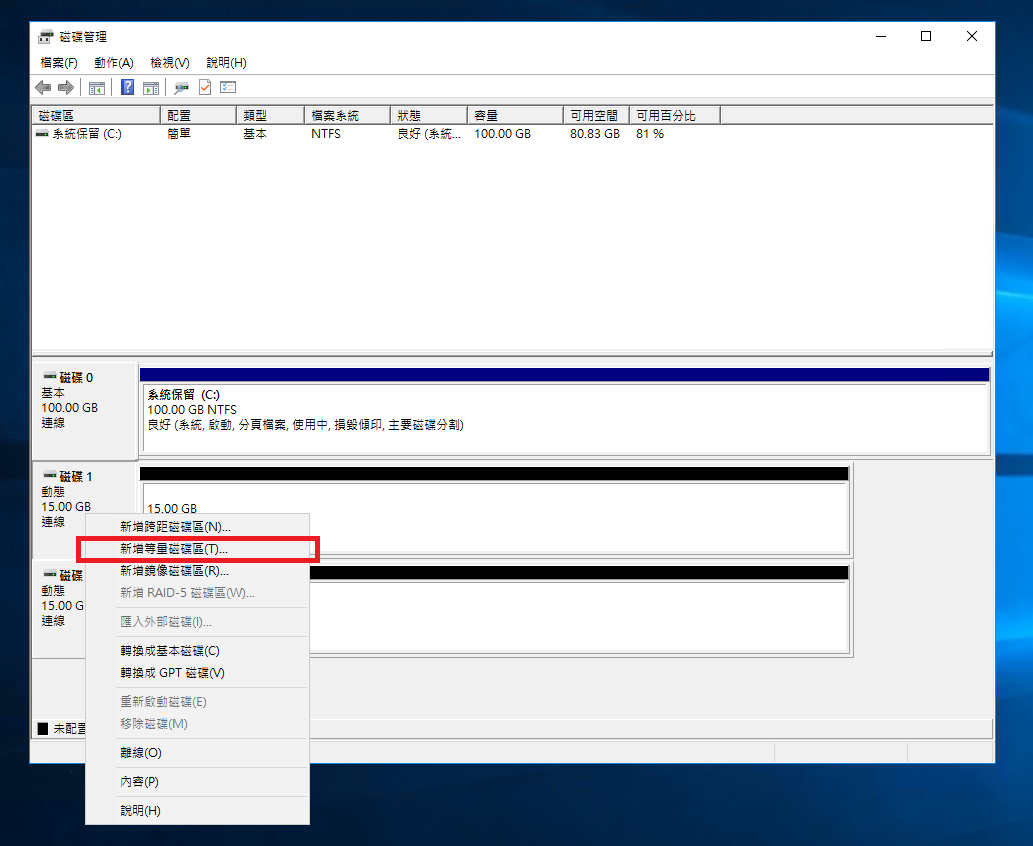
STEP 5 Configure RAID
Right-click Disk 1 and choose New Striped Volume to create RAID 0.
Select Disk 2 in the available disks list, then click Add.
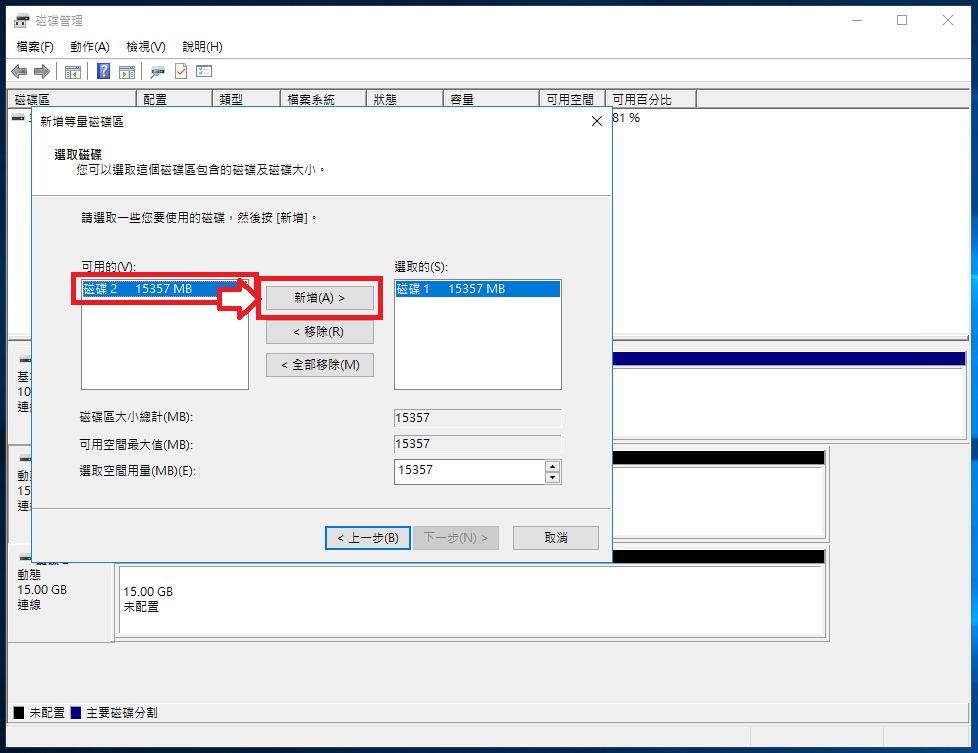
Click Next to confirm.
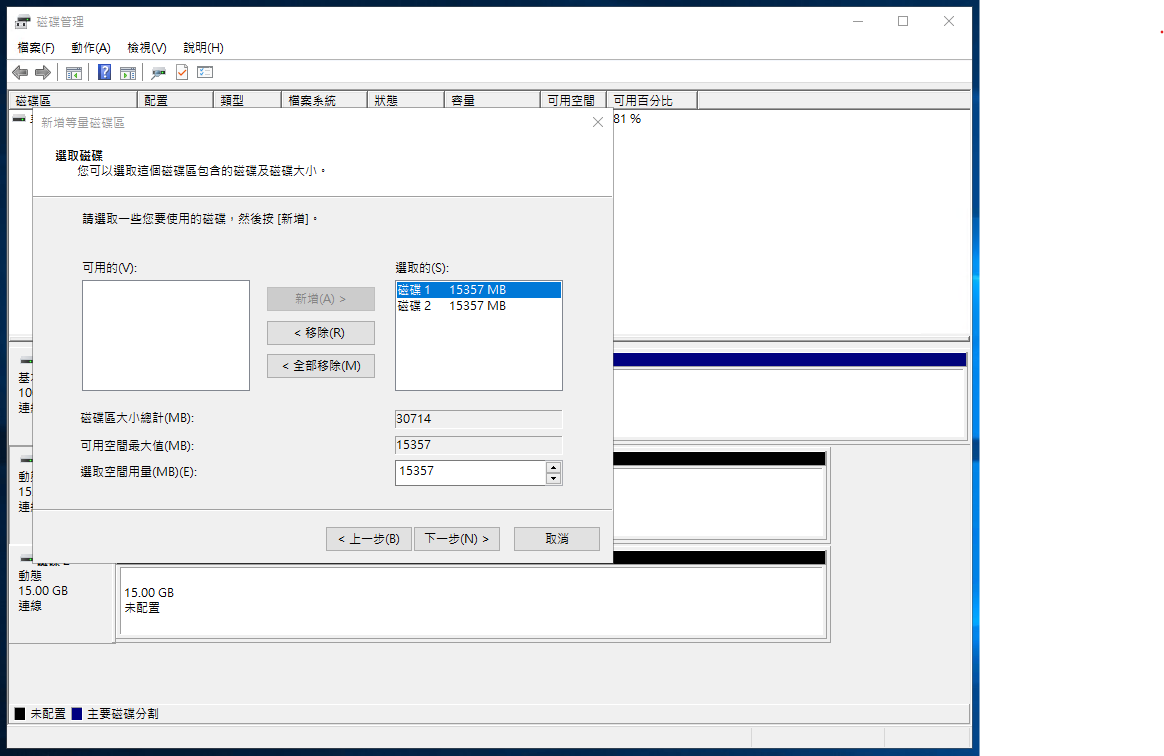
Select a drive letter for the RAID 0 volume.
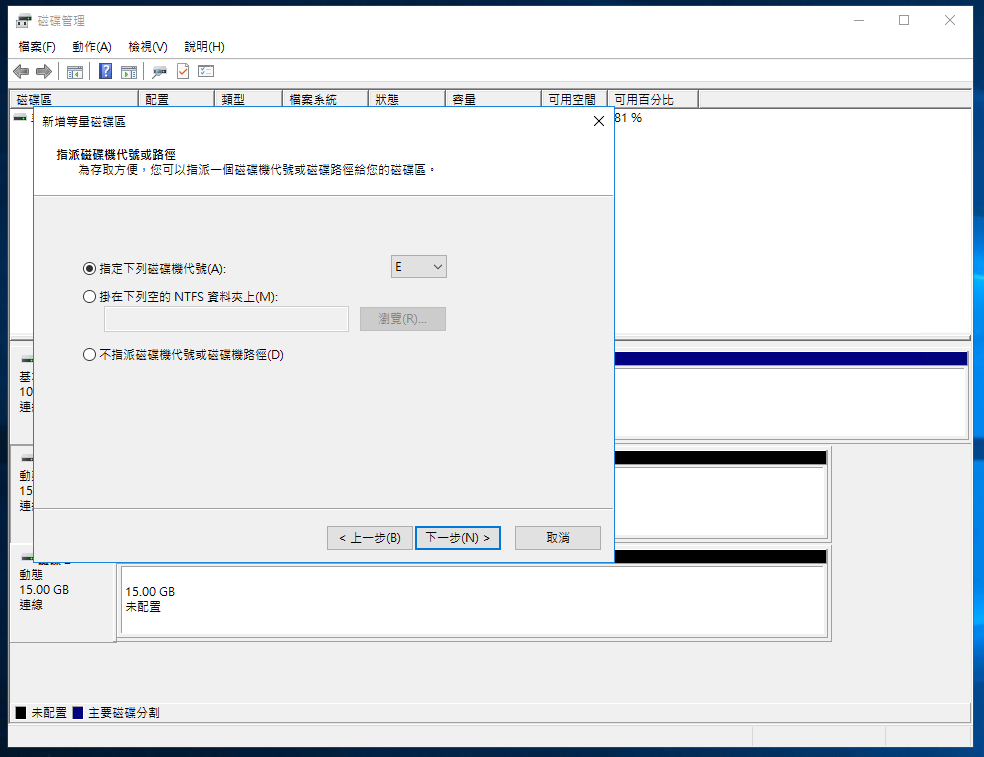
Set the formatting options and volume label, then check Perform a quick format.

After confirming the settings, click Finish.
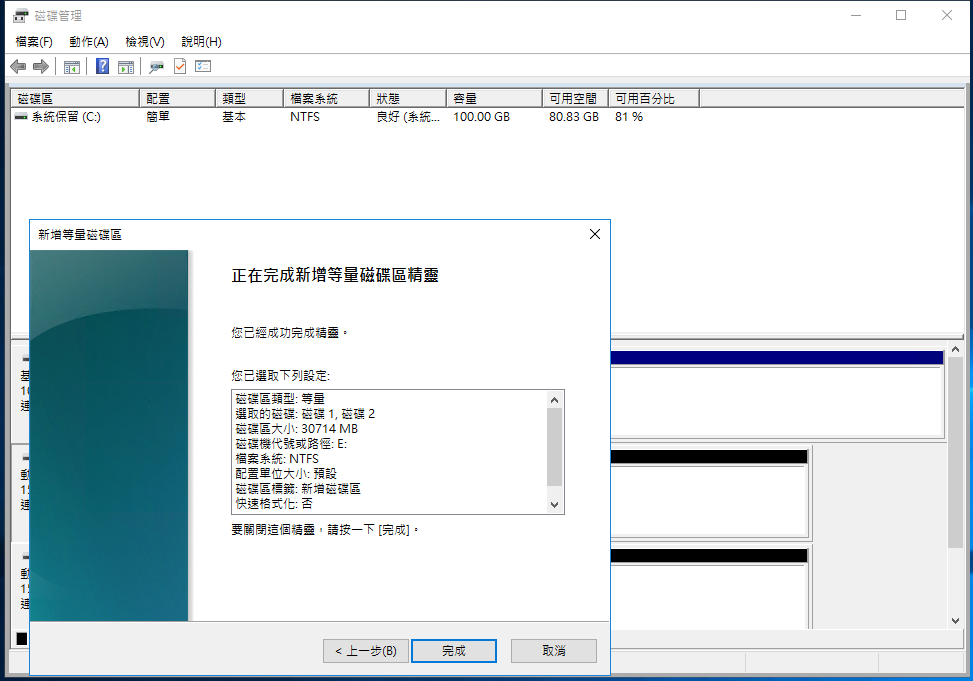
RAID creation complete:
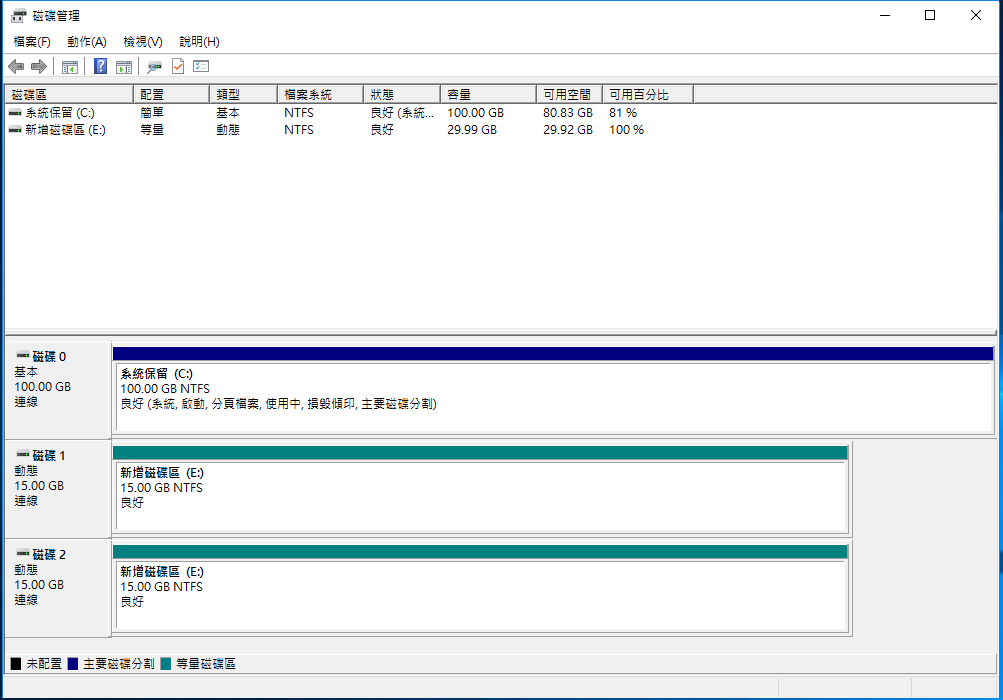
Verification
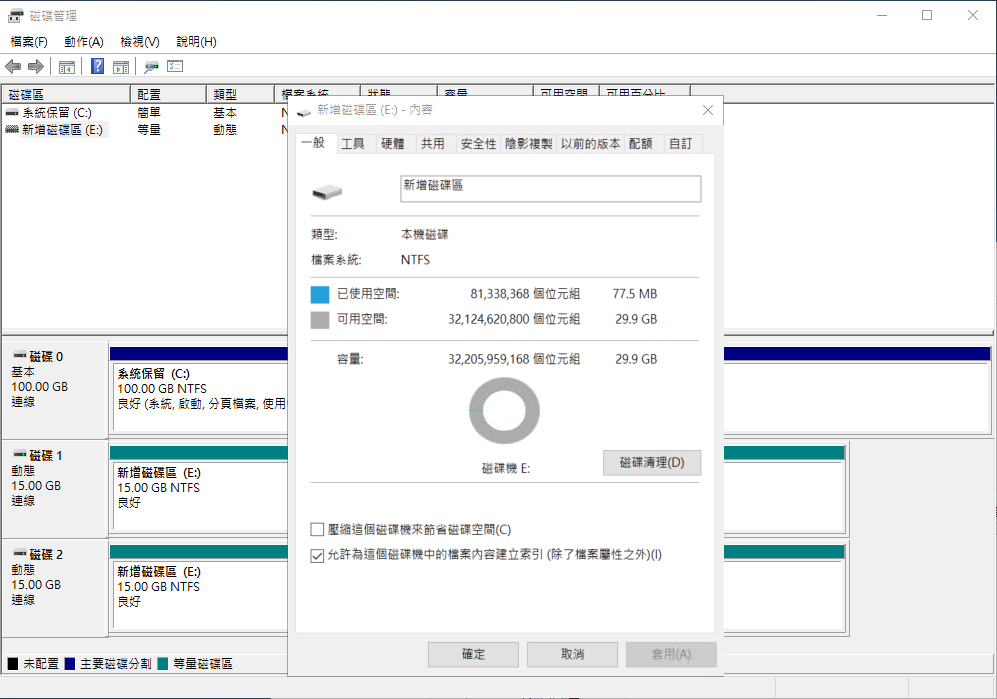
- Open the drive properties to confirm the capacity is correct.
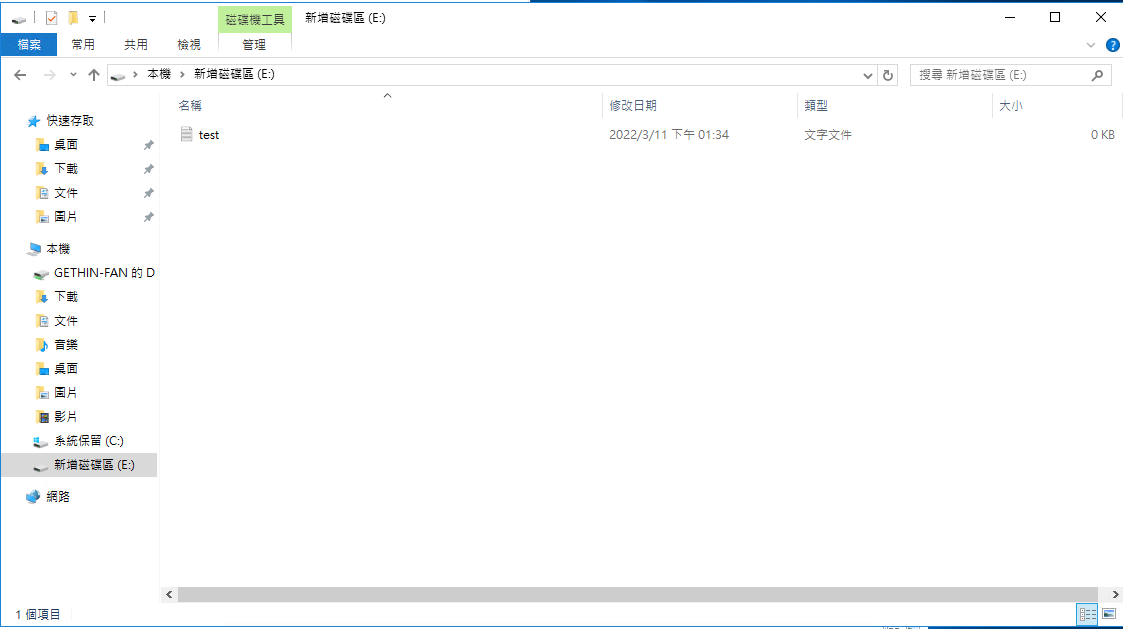
- Place files in the volume to test successful read/write
Notes
RAID 0 simply combines two disks into one larger storage device, doubling the capacity. However, it does not provide fault tolerance. If either disk fails, the entire RAID 0 volume will be corrupted, resulting in unreadable and unwritable data. Therefore, before choosing RAID 0, carefully evaluate whether you can accept the risks associated with it.
Image source: pexels

