Currently, all container environments provided by TWCC use GPU resources. However, in some use cases, GPU computing power is not necessary. Launching a development-type container for such purposes would result in unnecessarily high computational costs. This article explains how to build a container environment on TWCC that uses CPU computing resources.
Introduction
This article will introduce how to set up a Docker container environment using virtual computing entities to meet the needs of using CPU container environments. This article uses the Linux operating system for deployment and the machine learning framework TensorFlow as an example.
Prerequisites
TWCC v.super (2 CPU, 16 GB memory, 100 GB HDD) Virtual Compute Service instance
Detailed Steps
1. Update Packages
sudo apt update
2.Install Docker (it is recommended to follow the official installation guide
wget -qO- https://get.docker.com/ | sh
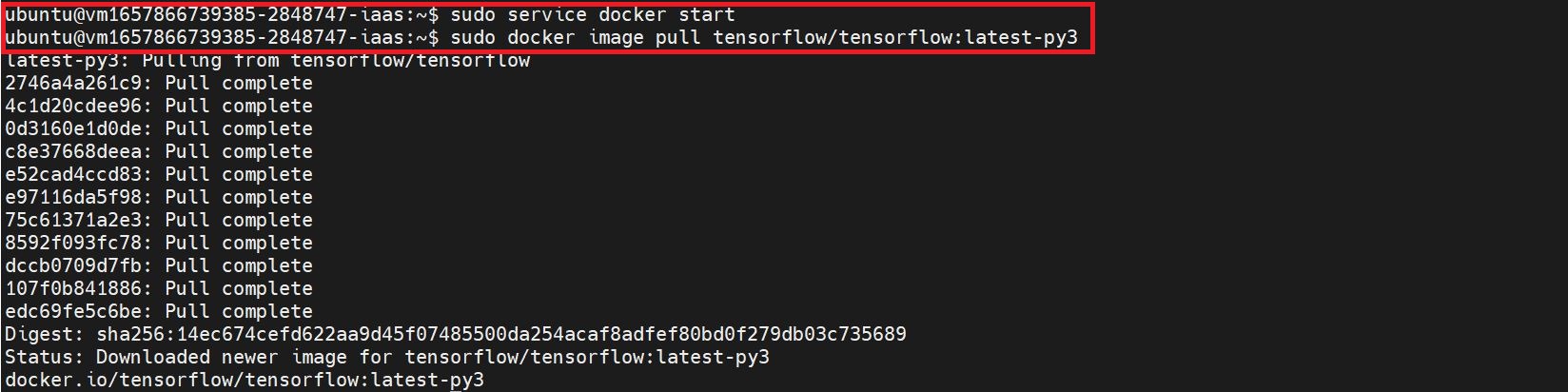
3. Start the Docker Service and Pull the Image
sudo service docker startsudo docker image pull tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-py3 - make sure to select the CPU version of the image file.
4. Run the Docker Environment
sudo docker run --name tensorflow -it tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-py3 bash
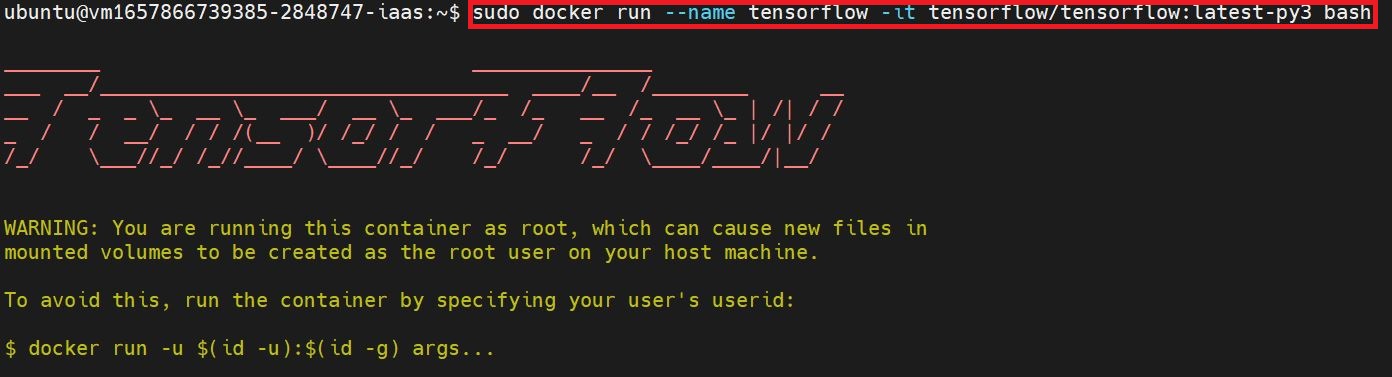
If you need to use Jupyter Notebook, please continue with the following steps.
Make sure that the virtual compute instance has opened the default Jupyter Notebook port 8888. You can refer to theSecurity Groupsdocumentation for instructions.
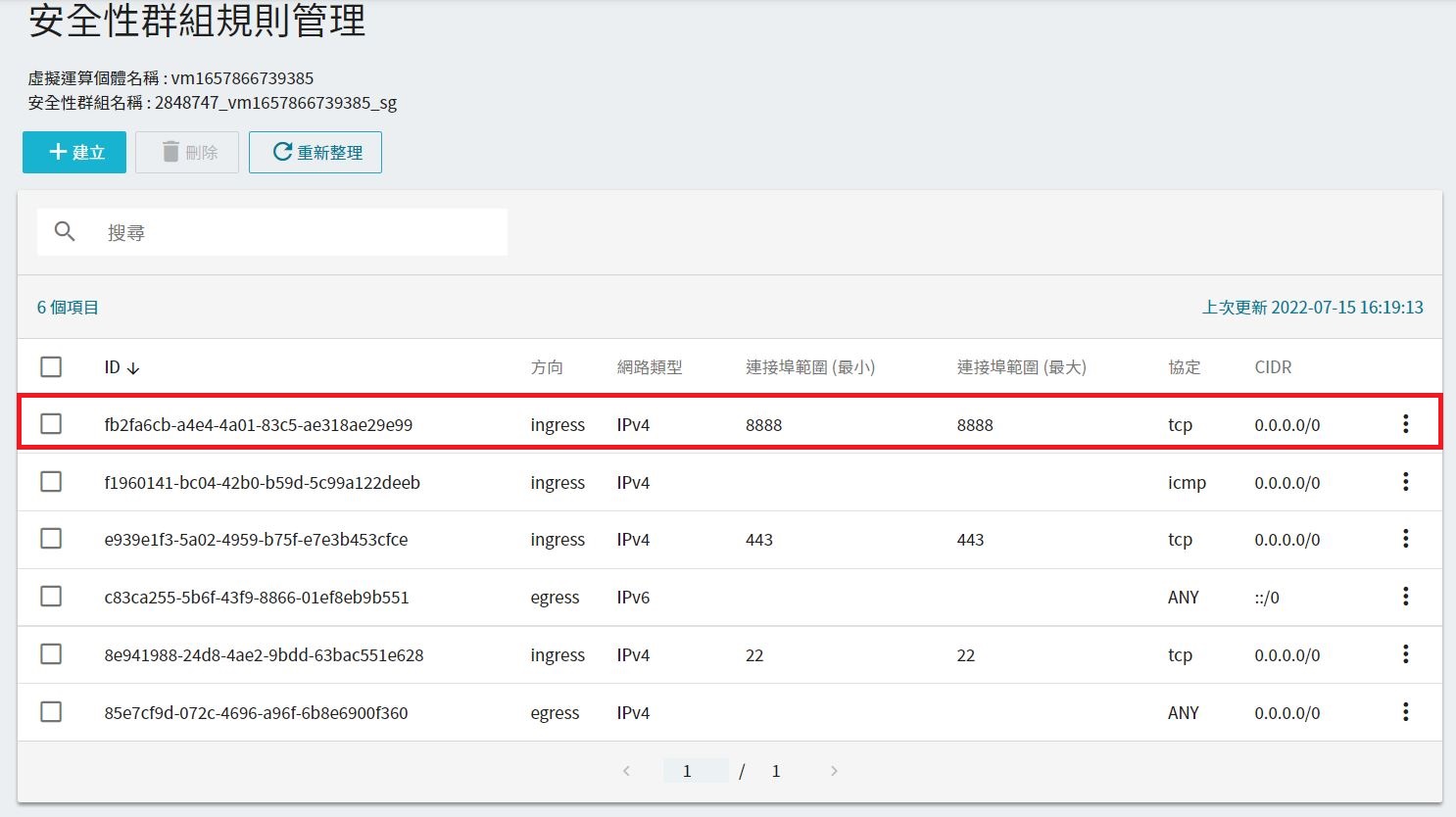
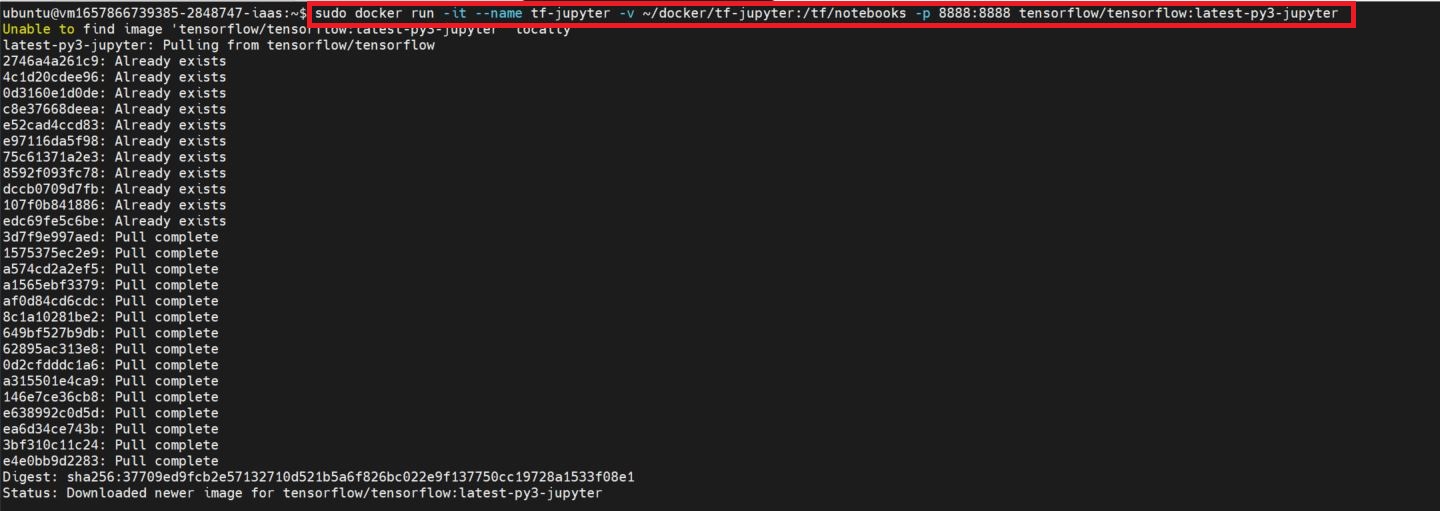
5. Use the TensorFlow Jupyter Image to Create a Container
docker run -it --name tf-jupyter -v ~/docker/tf-jupyter:/tf/notebooks -p 8888:8888 tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-py3-jupyter
6. Obtain the Jupyter Notebook Link and Modify the IP
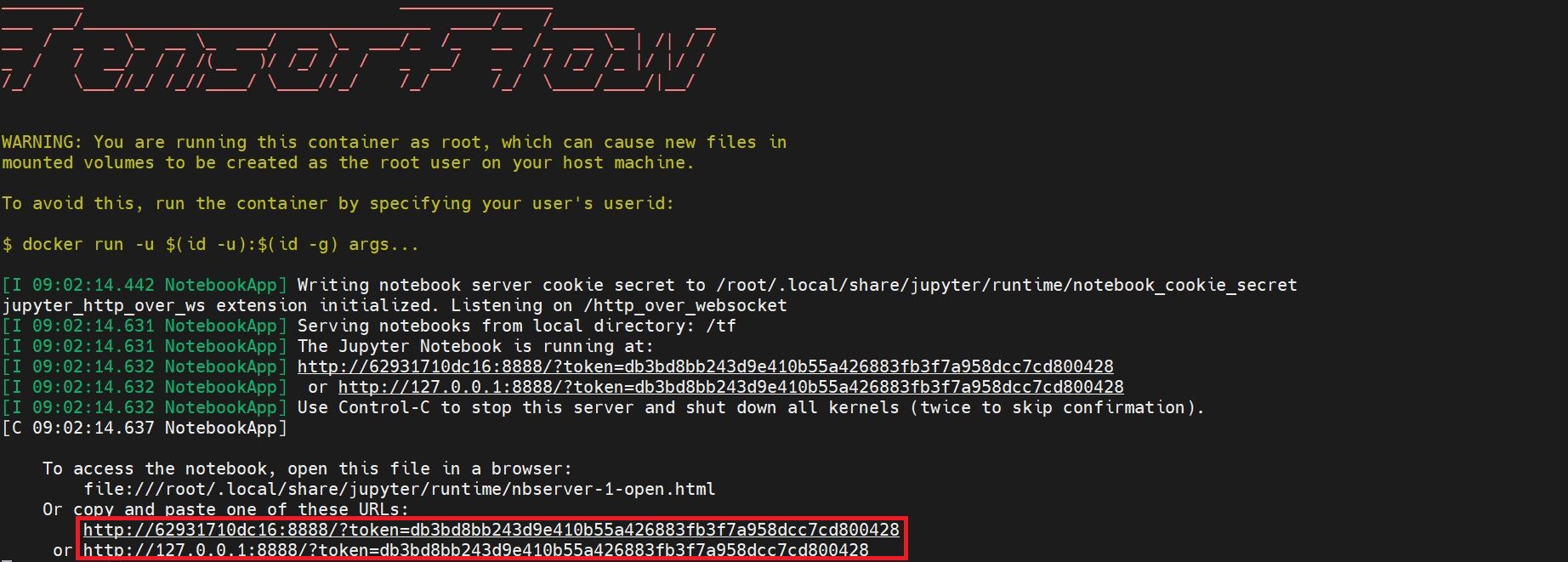
Copy the link highlighted in red and replace the container ID or local IP with the public IP of the virtual compute instance. The IP format is: http://:8888/
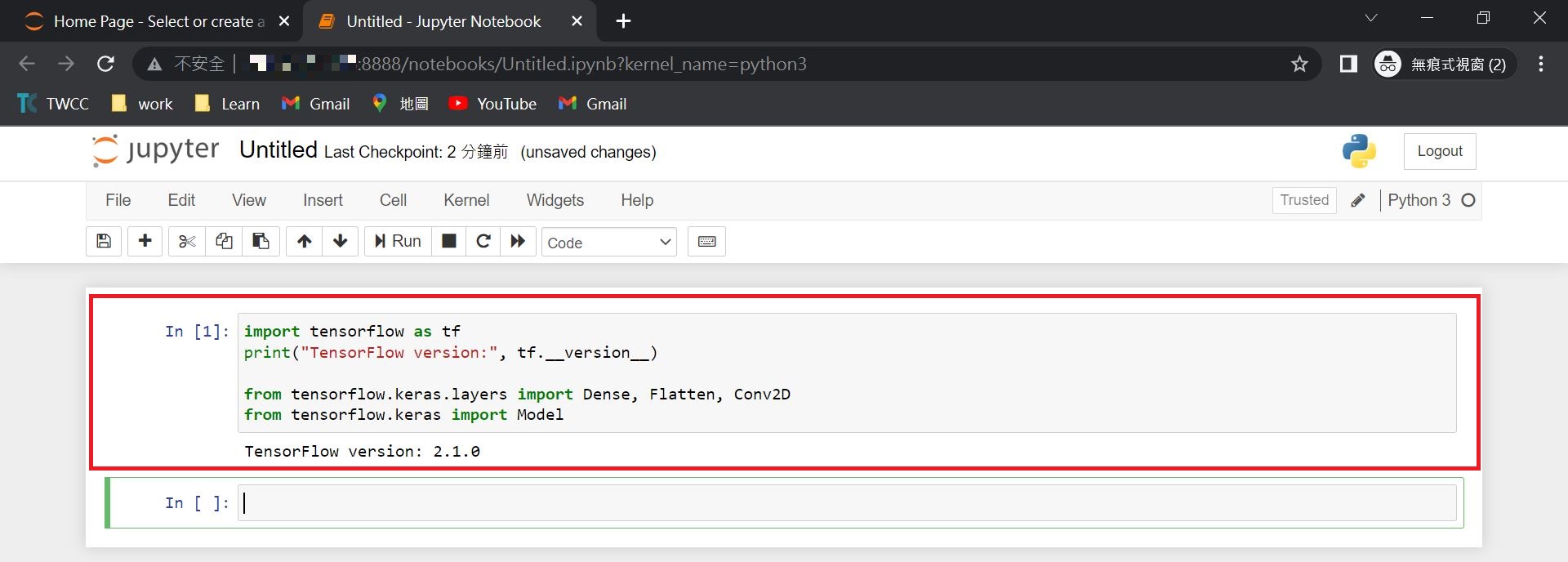
7. Verify the Connection